
When we talk about small satellite applications, we are basically answering this question: What are they for? It may seem like a simple and straightforward question, but books on the subject could be written. It's the same as wondering what the Internet is for. The list of possible answers is endless. We all understand that it is not the same to ask that question in 2004 or to ask it right now. In both cases we are talking about sectors in constant evolution, since every year new businesses in space appear and also on the Internet.
Space has become an accessible place. The evolution of technology and the emergence of small satellites have meant that startups, SMEs, large companies and emerging countries can reach space in an affordable way and within short periods of time, in a position to compete with traditional players in the sector. It's what is known as the New Space age.
If we are talking about small satellite applications, everything comes down to this question: What do you want, and what can you carry as a payload in nanosatellites? Of course, that answer depends on the evolution of technology, your needs... and your imagination. Within the businesses in space that can be developed with the help of nanosatellites, there are massive sectors and also market niches.
But let's cut to the chase. For this article we have chosen 26 small satellite applications that are already a reality or are on their way to becoming one, although we have no doubt that if we were asked this same question in 10 or 15 years’ time, the answer will be very different ... and much more extensive.
We have grouped these 26 applications into six broad categories:
- Earth and Space Observation
- IoT and Communications
- Asset Tracking
- Science and Environment
- Security, Defence and National Space Programmes
- Other Small Satellite Applications
This list is intended to be more of a compilation of existing applications of small satellites than an exhaustive explanation of each of those possible uses. That is why we are going to be as brief, clear and concise as possible.
A. Earth and Space Observation
Nanosatellites usually operate in low orbits (LEO). The current technology makes it possible to have latest-generation cameras for capturing high-resolution images. We are talking about tools with dimensions that fit perfectly to the size of small satellites. In this type of project, the payload of the nanosatellites is usually the camera.
-
Capturing images of the Earth. One of the most widespread uses of small satellite constellations. There are several companies working on obtaining high quality images of our planet. This is the case of a number of giants in the New Space sector, such as Planet Labs, which has put more than 330 satellites in orbit since 2013.
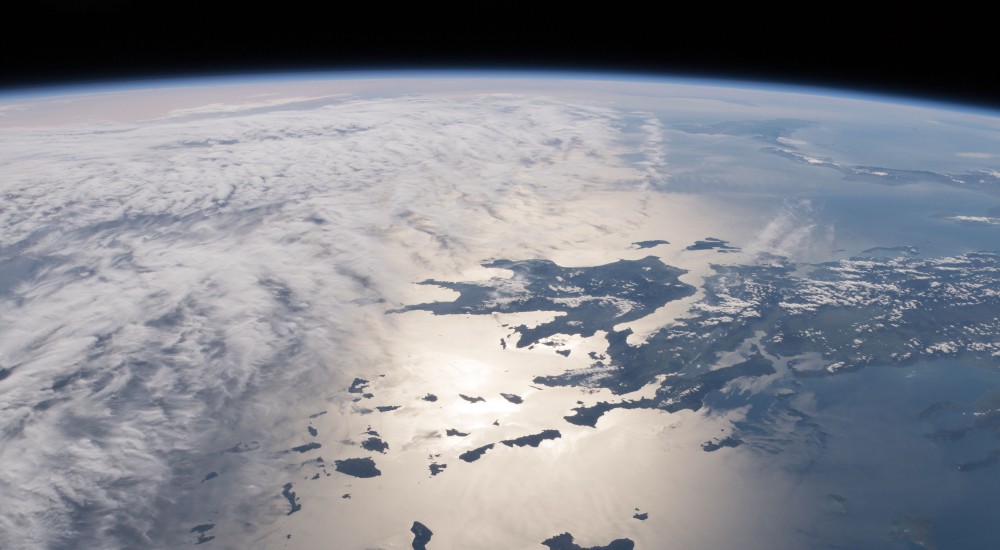

Greece and the Aegean and Ionian Sea / Photo: NASA, April 2018. Cropped image. -
Earth mapping. Satellites have also revolutionized the field of cartography. From the most remote to the most populated areas on Earth, small satellites provide accurate and up-to-date maps of the entire planet.
-
Astronomy. It's the other side of the coin when it comes to observation projects. We have already seen that high resolution images of the Earth can be captured, but there are also services that point in the opposite direction: the use of small satellites to obtain information and images of outer space. A few months ago, for example, the CubeSat ASTERIA successfully completed its mission of measuring the transit of an exoplanet known as 55 Cancri e. Another proposal underway in this field involves the use of small satellites as “guide stars” for latest generation telescopes, which require stable references to investigate and obtain quality images of distant planets and celestial bodies.
B. IoT and Communications
The Internet of Things (IoT), machine-to-machine communication (M2M), telephony and Internet access have become some of the most common small satellites applications. Space has become an ideal solution to improve the efficiency of existing terrestrial communication networks, which have obvious limitations in their coverage.
In these projects, the satellite payload would be a device capable of receiving, storing and processing information. For example, an SDR platform (Software Defined Radio). Let's take a look at some of these services:
-
IoT and M2M communications. By 2025 it is estimated that there will be more than 25.2 billion IoT connections worldwide and that the global market for this sector will reach 950 billion euros. IoT-based business models require real-time information on all types of sensors and connected devices, a terrain where small satellite constellations can be key, especially in isolated or difficult-to-access areas. From space you can receive, store and forward information to any point in real time.
-
Remote management. Through sensors, it is possible to remotely control the correct operation of all types of devices. It's not just about receiving the information, but also sending commands for certain settings or configurations remotely, virtually in real time and anywhere on the planet, no matter how isolated. Think of projects in hard-to-reach areas such as Antarctica, the Amazon basin or offshore platforms, or critical infrastructure such as nuclear power plants, where land-based communications are supported by satellite communications.
-
Communication in isolated areas. In the 21st century, there are still places on the planet that are virtually uncommunicated: large rural areas, frozen areas, desert territories, jungle areas, the high seas... In this field, small satellites offer very interesting solutions to guarantee communication in all circumstances.
-
Mobile telephony. Unlike the previous section, we are already talking about the whole planet, not just remote areas. At a time when we can say that smartphones have transformed our lives, there are mobile phone projects from companies such as Sky and Space Global, to ensure stable and secure communication, with global voice, data and instant messaging services.
-
Repeaters for radio amateurs. Small satellites have also demonstrated their ability to function as communications repeaters for the three million registered amateur radio operators worldwide.
-
Internet access. According to data from a year ago, only 55.1 percent of the world's population has access to the Internet. There is a significant technology gap, favouring richer countries and urban areas. Today, several projects have already been launched to provide universal access to the Internet, even in remote locations. Once again, small satellites are playing a key role in that revolution.
C. Asset Tracking
Geolocation and space have been closely related for years. There are systems such as GPS, Galileo, GLONASS or BeiDou. In the case of nanosatellites, asset tracking, as we saw a few days ago in this blog, is also one of its main fields of action.
As in IoT and communications applications, the payload in asset tracking projects has to be a device capable of collecting the information sent from the Earth, storing it and transmitting it back to Earth stations. Small satellites are an ideal solution to guarantee a stable, precise service with total coverage anywhere on the planet. What are the main practical applications of small satellites in this field? Let's see the most important ones.
-
Fleet management. Satellite tracking of all types of vehicles (cars, trucks, buses, industrial machinery...) has been a reality for years. Nanosatellite constellations also have the ability to reinforce traditional networks and provide solutions for precise control of vehicles and mobile resources, even in isolated areas.
-
Logistics. From products with a value of just a few cents to others that can cost several million euros, logistics companies move an enormous amount of goods every day. Today we are used to knowing the location in real time and the estimated time of arrival of any product, no matter its price. All the more so if we are talking about logistics containers, luxury goods, machinery or very valuable or delicate goods, which may require controlled transport conditions (temperature, movement...) and various means of transport to reach their destination (road, rail, airplane, ship...), from one side of the planet to the other. Small satellite constellations are also an effective solution to improve security, control and traceability in the logistics sector.
-
Ship tracking (AIS). The use of small satellites is a solution that helps to improve the safety of all types of vessels and to control some problems that often affect maritime traffic. Think of illegal fishing or piracy, for example. S-AIS systems (Satellite-Based Automatic Identification Systems) are available for this purpose. With the help of nanosatellites, it is possible to compensate for the limitations of terrestrial networks, especially in areas of low coverage, and to ensure at all times the location and control of vessels.
-
Aircraft tracking (ADS-B). ADS-B (Automatic Dependent Surveillance - Broadcast) terrestrial systems provide accurate information in seconds in very well communicated areas. It's not the same in remote areas. Some of the biggest air tragedies of recent years have to do with the disappearance of planes in shaded areas. There are already nanosatellite-based solutions for ADS-B systems that make it possible to increase safety, improve air traffic control, receive certain information provided by flight sensors in real time and know at all times the exact location of the aircraft.
D. Science and Environment
This is a very broad category. From a radar to a micro-laboratory for experiments in space, in these applications the payload of satellites depends on the objectives of each project.
-
Meteorology. Small satellites are called upon to play an important role in storm detection and in the development of climate and weather models that help improve weather forecasts. For example, NASA has already entered the testing phase of the RainCube project (Radar in a CubeSat), for the location, tracking and analysis of rain and snow storms all over the planet.
-
Protection of the environment. This is a type of practical application that affects us closely, due to the participation of the Alén Space team in the development of the nanosatellite Lume-1 within the European project FireRS. In this case, the objective is the early detection and monitoring of forest fires, but there are many other solutions based on small satellites related to the environment. Whether with optical instruments or sensors (IoT), we are talking about projects for the fight against ocean pollution, the detection of oil spills and spills, the monitoring of marine life, the control of desertification, the study of the progress of melting ice or the protection of areas of special environmental importance (such as the Serpens project, in the Amazon basin), among other initiatives.
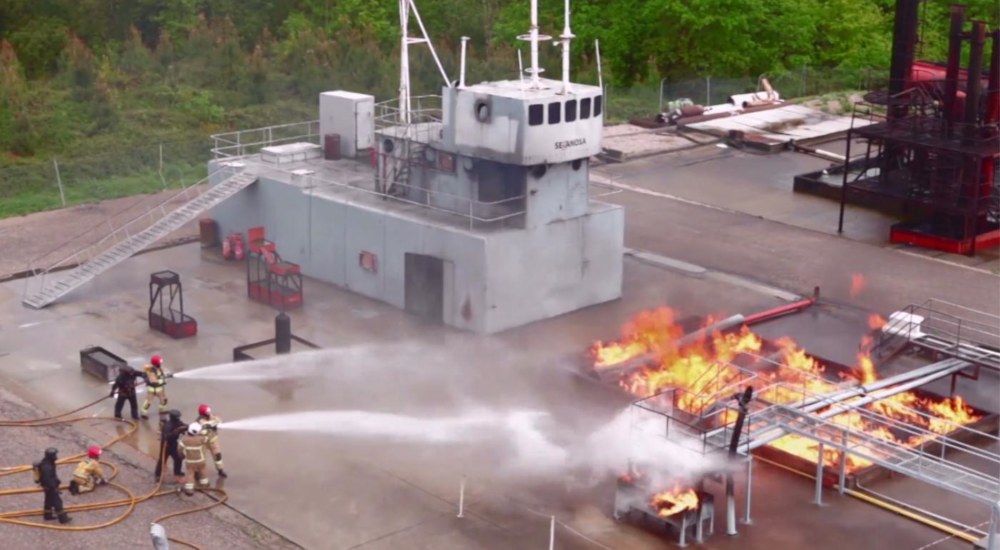

Demonstration of the European project FireRS / Photo: UVigo, April 2019. -
Agriculture. As in many other sectors, technology has also transformed the traditional concept of agriculture. Crop yield monitoring is another possible use of small satellites. Among the benefits, a better control of harvests, the improvement of the quality of agricultural products, the detection of diseases in crops, the evaluation by insurance companies of damage caused to harvests by certain meteorological events (storms, hail, floods...), or analysis of the repercussions derived from the periods of drought.
-
In-Orbit Demonstration. IOD (In-Orbit Demonstration) missions allow low-cost testing of space components. This practical application of small satellites fits perfectly with R&D projects, as a last step and guarantee before the commercialization of technology destined to be used later in space. We must not forget the enormous growth potential of the aerospace sector and the constant appearance of technological innovations. No element can be left to chance, so all that technology has to be tested in real conditions... or as real as possible. And what better way to make sure they will work in space than to test them in orbit?
-
Scientific projects. Small satellites have opened up space to companies and organizations that until recently could not dream of such an opportunity. The development of scientific experiments outside the Earth has become another common application of small satellites. Think, for example, of a research team that wants to develop a project related to the behaviour in space of certain technological or biochemical materials. The possibilities are enormous.
E. Security, Defence and National Space Programmes
For many years, space was a territory reserved for a handful of countries. Only the great superpowers could afford space programs and their own satellite networks, but the emergence of New Space has changed that forever.
The so-called democratisation of space has reached not only companies and startups, but also countries that want to launch their first space project or wish to strengthen their current capabilities. In some cases, these are programmes related to their national security, among others, for action in emergency situations.
-
Signals Intelligence (SIGINT). If we are talking about monitoring the radioelectric and electromagnetic spectrum, the practical applications of nanosatellites are very varied. Think of identifying signals from the Earth and space, monitoring communication traffic patterns, detecting interference and locating its origin, preventing the illegal use of radio bands and unauthorized emissions, etc.
-
Prevention, disaster management and humanitarian aid. In crisis situations, such as earthquakes, tsunamis or hurricanes, small satellites make it possible to act quickly, to immediately know the extent of the damage (even in isolated areas) and to manage relief and rescue teams. Preventive work is also possible. For example, a system of sensors and buoys in the ocean can detect in advance the arrival of a tsunami or a sensor in a reservoir can automatically generate a warning message in the event that the water reaches a dangerous level. With the support of nanosatellites, it is also possible to collect information and data from certain areas of the planet (not only in the case of natural disasters or specific emergency situations), which allow the planning of humanitarian aid.
-
Control of potential threats from outer space. If you've thought of asteroids and movies like 'Armageddon' have come to mind, you'll be surprised to learn that you're not too far off the mark. The applications of small satellites in this field have so far focused on the study and possible diversion of potentially dangerous asteroids for our planet, such as the Hera project of the European Space Agency (ESA). Science fiction comes true.
-
Space exploration. Within NASA's InSight mission, the MarCO A and B nanosatellites became in November 2018 the first two CubeSats to travel into deep space, with the mission to provide real-time telemetry of InSight's landing on Mars. This milestone has marked a starting point for small satellites to gradually gain prominence in the field of space exploration.
F. Other small satellite applications
We should not forget that the possible practical applications of small satellites are very extensive. All you have to do is have an idea... and get it up and running. In fact, there are projects for the development of business in space related to certain market niches, which do not fit into any of the previous sections.
-
Space mining. Some private companies have already begun to consider the exploitation of water, mineral and energy resources located in outer space. Last year, for example, a CubeSat was launched as part of a mission to locate and collect water in asteroids, with the aim of promoting future human expansion in space.
-
Space debris clean-up. The most modern small satellites are designed to enter the Earth's atmosphere once their mission is over, so that they disintegrate without leaving a trace, but this has not always been the case. Space debris can become a threat to satellites and space vehicles, but there are already projects with small satellites studying how this debris can be removed, such as the RemoveDebris mission.
-
Projection of advertising from space. You may have thought of the famous Batman warning sign, but this is not a comic or a movie. We are talking about a reality with several projects already underway for the projection of commercial messages in the night sky with the help of CubeSats.
-
Putting into orbit any object you can imagine. This application groups together all those business ideas that are based on the putting into orbit of anything that may pass through our mind. Let's start with the most exotic. Would we like our remains to rest forever in outer space? There is already a space funerals project that allows us to take our ashes or those of a loved one into space with the help of small satellites. Let's not forget the evocative power of space. Therefore, other business ideas also raise the orbit of more spiritual or romantic messages. Imagination is the limit.
The New Space sector is constantly expanding, and the forecasts point to an exponential growth of the businesses in space in the next years. Therefore, it is important to understand that these 26 possible applications of small satellites are only the tip of the iceberg that the future may hold.
Companies are beginning to assume that space is the last frontier of business... and that's an opportunity that's already here.
Featured image: NASA







Stay in Touch